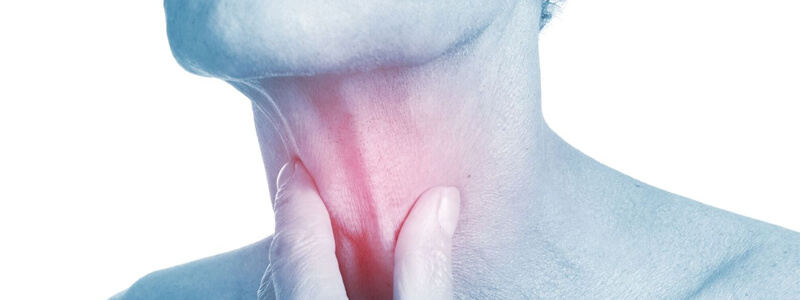
A 50-year-old man from India presents with neck pain, fevers and a large right-sided submandibular swelling. On examination the swelling is non-fluctuant and is situated below the angle of the jaw. The floor of his mouth appears oedematous. His temperature is 39.5 degrees C and he is tachycardic with a heart rate of 108 bpm. A photo of his neck is shown below:
1. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Show Answer
This patient has a diagnosis of Ludwig’s angina. Ludwig’s angina is a very serious and potentially life-threatening cellulitis in the submandibular area. It most commonly occurs due to infection in the floor of the mouth, which migrates into the submandibular space.
The clinical features of Ludwig’s angina include:
- The patient is generally very unwell with features of sepsis present
- A non-fluctuant submandibular swelling is usually present
- Oedema of the floor of the mouth and around the larynx
- Elevation and posterior displacement of the tongue
- Signs of airway obstruction may be present
Image sourced from www.wikipedia.org
Show Answer
Numerous organisms can cause Ludwig’s angina and approximately 50% of cases are polymicrobial. The two commonest causative organisms are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus viridans.
Other implicated organisms include:
- Bacteroides spp.
- Klebsiella spp.
- Pseudomonas spp.
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Escherichia coli
3. What are the risk factors for developing this condition?
Show Answer
Risk factors for Ludwig’s angina include:
- Poor dental hygiene
- Recent dental procedures
- Diabetes mellitus
- Immunosuppression
- Alcoholism
4. Which potentially life-threatening complication should you be concerned about?
Show Answer
Airway compromise can occur rapidly and all patients with suspected Ludwig’s angina should be sent to the nearest Emergency Department by ‘blue light’ ambulance immediately. Once in a safe ‘resus area’ the management priorities are airway safety and sepsis management.
Header image used on licence from Shutterstock






very useful..Thanks
Thank you very useful
Fine detailed evaluation of the condition,worth reading.Thank you so much