Articles
Thyroid Storm
Thyroid storm, also known as thyrotoxic crisis, is a rare but life-threatening condition characterised by an extreme exacerbation of thyrotoxicosis symptoms. It occurs in approximately 1-2% of patients with established hyperthyroidism. This medical emergency demands...

Antifreeze Poisoning
Ethylene glycol, a component commonly found in antifreeze, presents a serious toxicological emergency. Though it initially acts like ethanol, its metabolism leads to highly toxic acid by-products, resulting in multiorgan damage if not recognised and treated early....
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions are exaggerated or inappropriate immunologic responses occurring in response to an antigen or allergen. Gell and Coombs described four classes in 1963: Type I hypersensitivity reactions Type II hypersensitivity reactions Type III...
Life Threatening Chest Injuries in Trauma – The Killer Six
Trauma remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, with chest injuries representing a significant portion of these cases. Whether resulting from motor vehicle accidents, falls, or penetrating trauma, injuries to the chest can lead to immediate compromise of vital...

What Killed George Washington?
George Washington is undoubtedly one of the world's most famous historical figures. He served as the Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army during the American War of Independence, presided over the 1787 convention that drafted the United States Constitution, was...
Methaemoglobinaemia
Methaemoglobinaemia occurs when red blood cells contain methaemoglobin at levels higher than 1%. Methaemoglobinaemia results from the presence of iron in the ferric form instead of the usual ferrous form. The ferric form is unable to bind oxygen, and its presence...

Understanding the APGAR Score
The Apgar score is a simple method of assessing a neonate’s well-being at birth. There are five criteria, each of which is allocated a score between zero and two. The assessment is generally performed at one and five minutes after delivery, and may be repeated later...
John Snow and the 1854 Cholera Outbreak
In August 1854, Soho in London was struck with a severe cholera outbreak. Cholera is a gastrointestinal infection caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. It is still prevalent in areas with inadequate sanitation and poor food and water hygiene and remains a...
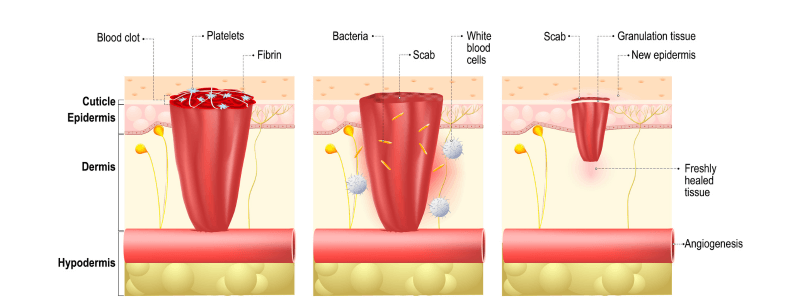
Wound Healing
Wound healing, as a normal biological process in the human body, is achieved through four precisely and highly programmed events: haemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodelling. For a wound to heal successfully, all four phases must occur in the proper...
Mastering the Symphony of the Heart: A Comprehensive Guide to the Heart Sounds
The heart produces a symphony of sounds that can provide valuable insights into a patient's cardiovascular health. This article will delve into the fundamental principles of heart sounds, their physiological basis, and their clinical significance, equipping medical...




