


Togo and the Diphtheria Serum Run
Thanks to modern childhood vaccination programs, diphtheria is now a rare illness in Western Europe and the United States. It is still common, however, in developing countries where vaccination rates are low. It is a terrifying illness caused by the airborne bacterium...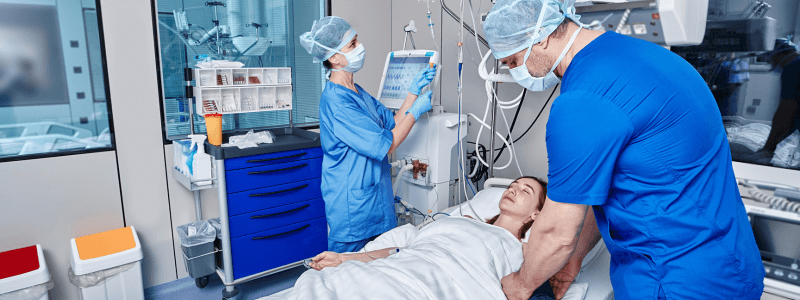
Addisonian Crisis
An Addisonian crisis, also known as an adrenal crisis, is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition that arises due to acute adrenal insufficiency. It is a rare condition with an estimated prevalence of around 600 per million, but it does present to the...
Cardiac Arrest in Pregnancy: Critical Considerations
The management of cardiac arrest during pregnancy presents unique challenges that demand specialised knowledge and swift action. Maternal cardiac arrest is a rare but high-stakes scenario that requires a comprehensive understanding of resuscitation techniques tailored...
Thyroid Storm
Thyroid storm, also known as thyrotoxic crisis, is a rare but life-threatening condition characterised by an extreme exacerbation of thyrotoxicosis symptoms. It occurs in approximately 1-2% of patients with established hyperthyroidism. This medical emergency demands...




