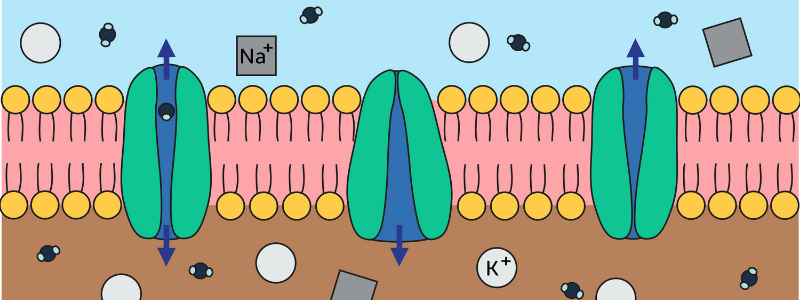
Sympathomimetic Drugs
Sympathomimetic drugs are stimulant compounds that mimic the effects of endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system. These drugs are used in a variety of situations, including cardiac arrest, haemorrhage, sepsis and myocardial insufficiency. Mechanism...
Hypothermia
Hypothermia exists when the core body temperature is below 35°C and is classified arbitrarily as mild (32-35°C), moderate (28-32°C), or severe (<28°C). The Swiss staging system, based on clinical signs, can be used by rescuers at the scene to describe victims: I –...
Heat Stroke
Heat stroke is defined as a systemic inflammatory response with a core temperature that is greater than 40.6°C accompanied by a change in mental state and varying levels of organ dysfunction. There are two forms of heat stroke: Classic non-exertional heat stroke –...
The Story of the Tendon Hammer
The tendon hammer is one of the most historically resilient medical instruments still in use today. It is a simple yet invaluable device that can be used to diagnose a wide variety of nervous system and muscular disorders. Almost 130 years after the invention of the...