Hepatitis B Serology and Vaccination
Hepatitis B is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), a double-stranded DNA virus of the Hepadnaviridae family that replicates by reverse transcription. Hepatitis B is the most common cause of hepatitis globally, and the World Health...
Practice Questions for the PLAB Part 1
The Professional and Linguistic Assessments Board (PLAB) test is the main route by which International Medical Graduates (IMGs) demonstrate that they have the necessary skills and knowledge to practice medicine in the UK. The PLAB Part 1 is a computer-based exam that...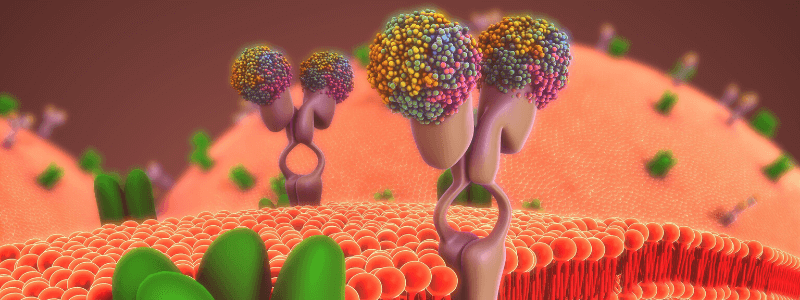
Cell Structure and Function Part 2 – The Cell Membrane
In Part 1 of our ‘Cell Structure and Function’ series we learnt about basic cell structure and the organelles. We now move on to the cell membrane and membrane transport. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, physically separates the inside of the cell...
Cell Structure and Function Part 1 – The Organelles
The cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism, it is the functional and structural unit of all living things and all living structures in the human body are made of cells. The human body contains several billion cells, encompassing a vast range of types...