Articles

Maternal Changes During Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a period of profound physiological transformation. The mother’s body undergoes wide-ranging adaptations across virtually all organ systems, designed to support foetal growth, prepare for labour, and safeguard maternal well-being. These changes are...
Pregnancy
Pregnancy, also referred to as gestation, is the period during which one or more offspring develop inside the uterus. It typically lasts around 40 weeks from the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP) and is divided into three trimesters. The first...
Conception
Following the deposition of sperm in the vagina at the cervix, it is subsequently transported to the uterus. Here it fertilises the ovum and implants in the uterine stroma, and this process is known as conception. Transport of sperm Immediately after...
Sexual Intercourse
Sexual intercourse, which is also referred coitus or copulation, is the reproductive act in which the male reproductive organ enters the female reproductive tract. Upon completion of the reproductive act, sperm cells are passed from the male body into the female,...
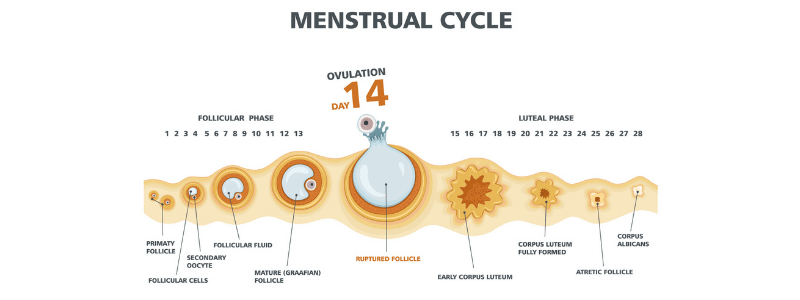
The Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is the regular cycle of vaginal blood loss (menstruation) that results from the breakdown of the uterine lining when the implantation of a fertilised ovum does not occur. Menstruation occurs on a monthly cycle throughout a woman's reproductive...

Puberty
Puberty is the process by which a child's body matures into an adult body and becomes capable of sexual reproduction. It is a complex process involving both physical growth and sexual and psychosocial maturation. Puberty usually begins between 8 and 14 years of age in...

Thomas Linacre and the Royal College of Physicians
The Royal College of Physicians is a U.K. based, internationally recognised, professional body that is dedicated to the improvement of medical practice and patient care. It is also the oldest royal medical college in the world. In 2006 I became a member of the Royal...
Sympathomimetic Drugs
Sympathomimetic drugs are stimulant compounds that mimic the effects of endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system. These drugs are used in a variety of situations, including cardiac arrest, haemorrhage, sepsis and myocardial insufficiency. Mechanism...

Hypothermia
Hypothermia exists when the core body temperature is below 35°C and is classified arbitrarily as mild (32-35°C), moderate (28-32°C), or severe (<28°C). The Swiss staging system, based on clinical signs, can be used by rescuers at the scene to describe victims: I –...
Heat Stroke
Heat stroke is defined as a systemic inflammatory response with a core temperature that is greater than 40.6°C accompanied by a change in mental state and varying levels of organ dysfunction. There are two forms of heat stroke: Classic non-exertional heat stroke –...




